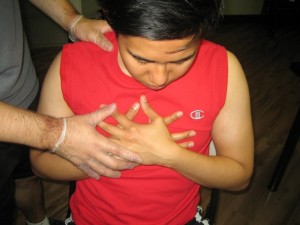
A bronchospasm is tight contraction of the bronchial muscle which causes narrowing of the bronchi and becomes worse when the mucous membrane is swollen and inflamed. Sticky mucus coming from the bronchial glands can cause obstruction in the bronchi and can be difficult to force out when coughing.
Bronchospasm is a common characteristic of asthma but other conditions such as respiratory infections, emphysema, chronic disease of the lungs, chronic bronchitis, anaphylactic shock, food allergies, chemicals and insect bites can cause irritation on the lungs.
Symptoms of bronchospasm
- Difficulty breathing especially at night and early in the morning while performing exercises.
- Wheezing or whistling sound especially while inhaling.
- Tightness of the chest and pain due to constriction of the air passage while the lungs and chest muscles becomes active to inhale air ends up strained and result to chest pain.
Difficulty breathing especially at night and early in the morning while performing exercises. - Explosive cough with sputum or can be dry which depends on the irritation and inflammation of the mucosal lining.
Causes
- Having a family history of allergy or asthma are at high risk of developing bronchospasm
- Upper or lower respiratory tract infections
- Irritants such as inhaling chemical smoke, cigarette smoke, strong odor and dry cold air.
- After performing strenuous exercises
- Emotional stress
Treatment
- Keep the affected person calm.
- Use the prescribed medications such as an asthma inhaler
- If the affected person is on a tracheostomy tube, let him/her suck on it. Stop if it disrupts breathing, change the tube if it is blocked and sucking could not remove the blockage.
- Perform rescue breathing or cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) if the heartbeat or breathing stops.
- Perform regular exercises that improves posture
- Drink plenty of fluids to replace lost fluids. Increased fluid intake lessens bronchi secretions that can be easily eliminated through coughing and deep breathing.
- Avoid prolonged laughing or crying to prevent overstimulation
- Perform relaxation techniques such as yoga and deep breathing to lessen tension in the body and promote fast healing of the condition.
- Take the prescribed expectorant for better drainage of the bronchial tree as well as lessen the viscosity of the sputum and provide relief from bronchospasm.
Tips
- If susceptible to bronchospasms while performing exercises, always warm-up and cool down for at least 15 minutes before and after workouts. Avoid exercising in very cold climate and if the pollen count is high.
- Breathe through the nose when suffering from cold to lessen irritation of the lungs by warming the air before reaching the lungs.
Disclaimer / More Information
The material posted on this page on bronchospasm is for learning purposes only. Learn to recognize and manage respiratory issues including bronchospasm by taking a first aid and CPR class with one of our training providers.